In today's competitive business world, leveraging data-driven strategies is not a luxury but a necessity. It is what separates industry leaders from laggards. At the core of these strategies is Business Analytics (BA). This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Business Analytics, discussing its importance, relevant tools and techniques, necessary skills, and the career opportunities it presents.

What is Business Analytics?
Business Analytics is a combination of skills, technologies, and practices for the continuous exploration and investigation of past business performance. It uses data and statistical methods to gain insights that inform business decisions and drive successful business planning.
In simpler terms, Business Analytics is all about turning raw data into valuable insights for your business. It helps organizations understand trends, patterns, and derive insights from the data to make better, informed decisions.
The Importance of Business Analytics
In the current data-driven world, Business Analytics plays a pivotal role in every sector - from healthcare to retail, finance, and even sports. Here are a few reasons why BA is so important:
-
Improved Decision Making: BA provides factual and data-based insights, which eliminates guesswork, and ensures decisions are grounded in evidence.
-
Efficiency and Productivity: BA can reveal bottlenecks in processes, helping businesses optimize operations for increased productivity.
-
Predictive Capabilities: Using predictive analytics, a subset of BA, businesses can anticipate customer behavior, market trends, and potential risks.
The Role of Business Analytics in Decision Making:
Business analytics plays a crucial role in decision-making by providing valuable insights and information to support informed choices. It involves analyzing data to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships, which can be used to gain a deeper understanding of business operations, customer behavior, market dynamics, and other relevant factors.
By applying various statistical and analytical techniques, business analytics helps organizations make data-driven decisions. It enables businesses to identify opportunities for growth, optimize processes, improve efficiency, and mitigate risks. Through data visualization and reporting, business analytics presents complex information in a clear and understandable manner, aiding in effective communication and decision-making.
Business analytics also assists in forecasting and predictive modeling, enabling organizations to anticipate future trends and outcomes. This proactive approach allows businesses to plan and strategize accordingly, optimizing resource allocation, pricing, inventory management, and marketing efforts.
Furthermore, business analytics facilitates the identification of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to monitor business performance. It provides a quantitative basis for evaluating the success of strategies, initiatives, and projects, enabling organizations to make adjustments and course corrections as needed.
Business Analytics Tools
Business Analytics cannot be conducted effectively without the right tools. Here are some of the most popular:
-
Microsoft Excel: A staple in data analysis, Excel offers powerful tools for data manipulation, analysis, and visualization.
-
Tableau: A popular data visualization tool, Tableau can handle massive datasets and create interactive visualizations.
-
Python: A general-purpose programming language, Python has become a favorite for data analysis due to its simplicity and powerful libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and SciPy.
-
R: R is a programming language and environment designed specifically for statistical computing and graphics.
-
SAS: A software suite developed for advanced analytics, multivariate analyses, business intelligence, data management, and predictive analytics.

7 Pillars of Business Analytics:
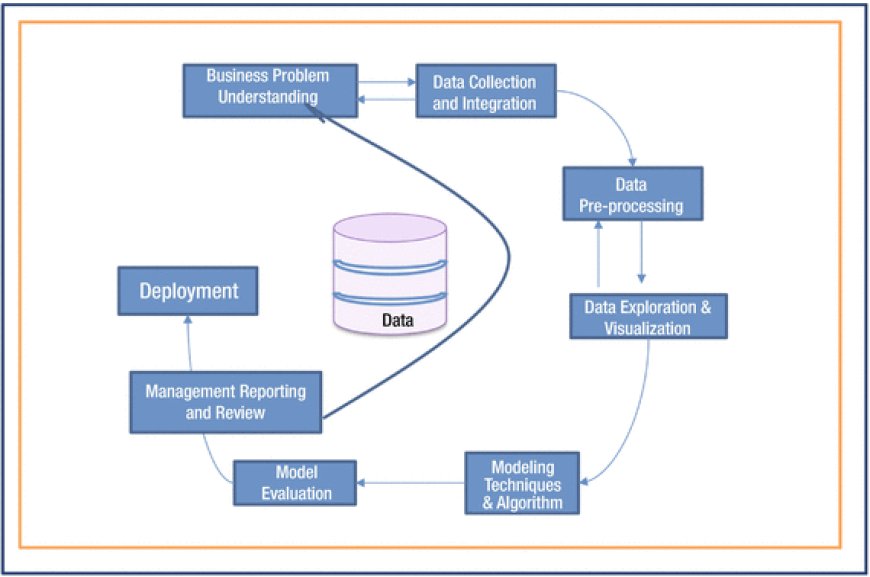
The seven pillars of business analytics provide a comprehensive framework for understanding and implementing effective analytics strategies. These pillars encompass various aspects of the analytics process, including data management, data exploration, statistical analysis, data visualization, predictive modeling, optimization, and deployment. By focusing on these pillars, organizations can ensure a holistic approach to leveraging data for informed decision-making. From collecting and managing data to exploring patterns, applying statistical techniques, visualizing insights, building predictive models, optimizing processes, and deploying solutions, each pillar plays a vital role in maximizing the value derived from business analytics. Together, they form a solid foundation for organizations to extract meaningful insights, drive actionable outcomes, and gain a competitive edge in today's data-driven business landscape.
The Dynamic Duo: Data Science and Business Analytics:
Business analytics and data science are two dynamic disciplines that complement each other in the realm of data-driven decision-making. While they share some similarities, they have distinct focuses and approaches.
Business analytics primarily emphasizes using data to drive strategic and operational decision-making within an organization. It involves analyzing historical data, identifying patterns and trends, and using statistical techniques to extract actionable insights. Business analytics focuses on understanding business processes, optimizing operations, and solving specific business problems. It often involves working with structured data, such as sales figures, customer data, or financial records.
On the other hand, data science has a broader scope and encompasses various techniques and methodologies for extracting insights from data. It involves collecting and processing data, applying advanced statistical and machine learning algorithms, and building predictive models. Data science often deals with both structured and unstructured data, including text, images, and sensor data.
Data science goes beyond analyzing historical data and aims to uncover hidden patterns, make accurate predictions, and drive innovation. It involves the application of programming skills, mathematical modeling, and algorithm development to tackle complex problems. Data scientists often explore new data sources, develop new algorithms, and work on cutting-edge technologies.
While business analytics focuses on applying analytics within a business context, data science has a broader application across industries, including healthcare, finance, marketing, and more.
Ultimately, business analytics and data science are intertwined disciplines that contribute to leveraging data for insights and informed decision-making. They complement each other in their approaches and tools, enabling organizations to extract value from data and gain a competitive advantage in today's data-rich landscape.
Essential Skills for Business Analytics
To succeed in the field of Business Analytics, certain skills are indispensable:
-
Statistical Knowledge: Understanding statistical concepts is crucial to interpret data and make informed decisions.
-
Data Visualization: The ability to present complex data in a visually intuitive manner is key to conveying insights to non-technical stakeholders.
-
Programming Skills: Familiarity with programming languages such as Python or R is essential for manipulating large datasets and performing complex analyses.
-
Machine Learning: With the rise of predictive analytics, knowledge of machine learning algorithms can be a game-changer.
-
Domain Knowledge: Understanding the industry where the analysis is being applied is crucial to formulate relevant questions and interpret the data correctly.
Finding The Right Business Analytics Courses:
Finding the right business analytics courses requires careful consideration of your learning goals, schedule, and preferred learning style. Start by researching reputable institutions or online platforms that offer business analytics courses. Look for courses that align with your specific areas of interest within business analytics, such as data visualization, statistical analysis, or predictive modeling.
Read course descriptions, syllabi, and reviews to understand the content and learning outcomes. Consider the level of the course (introductory, intermediate, or advanced) and ensure it matches your current skill level.
Evaluate the teaching methods and resources provided, such as interactive lectures, practical assignments, case studies, or access to relevant software and tools. Hands-on experience is crucial in business analytics, so prioritize courses that offer opportunities to apply the concepts through real-world projects or simulations.
Consider the flexibility and accessibility of the course. If you have other commitments, look for courses that offer flexible scheduling or self-paced learning options. Online courses can provide the convenience of learning from anywhere and allow you to progress at your own pace.
Take into account the credentials and expertise of the instructors. Look for courses taught by experienced professionals or academics who have practical industry knowledge in business analytics.
Lastly, seek recommendations from professionals in the field or join online communities and forums related to business analytics. These platforms can provide insights and recommendations on reputable courses and learning resources.
Understanding Descriptive, Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics:
Descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analysis are three distinct types of analytical approaches that provide valuable insights and guide decision-making processes.
Descriptive analysis focuses on understanding historical data and summarizing it in a meaningful way. It involves organizing and presenting data through charts, graphs, or statistical measures to gain insights into past events or trends. Descriptive analysis helps answer questions like "What happened?" and provides a foundational understanding of the data.
Predictive analysis, on the other hand, utilizes historical data to make informed predictions or forecasts about future outcomes. It involves applying statistical models, machine learning algorithms, or data mining techniques to identify patterns and relationships in the data. Predictive analysis helps answer questions like "What is likely to happen?" and provides insights that can guide decision-making by anticipating future trends or outcomes.
Prescriptive analysis takes the analysis a step further by recommending specific actions or strategies based on the insights derived from descriptive and predictive analysis. It combines data, optimization techniques, and business rules to generate actionable recommendations. Prescriptive analysis helps answer questions like "What should be done?" and provides decision-makers with actionable insights to optimize processes, allocate resources, or improve outcomes
Career Opportunities in Business Analytics
With the rising importance of data in decision-making, there is a growing demand for professionals skilled in Business Analytics. Here are some potential career paths:
-
Business Analyst: They work closely with businesses to identify problems and opportunities, using data analysis to inform business decisions.
-
Data Analyst: Data Analysts manipulate, process, and analyze large datasets to extract valuable insights.
-
Data Scientist: A step up from data analysis, Data Scientists use their knowledge in statistics and machine learning to make predictions about future events.
-
Business Intelligence Developer: They design and develop strategies to assist businesses in interpreting raw data and deriving meaningful insights.
The Rise of Business Analytics in Job as Paragraph:
The rise of business analytics has led to a significant increase in job opportunities across industries. As organizations recognize the value of data-driven decision-making, the demand for professionals skilled in business analytics has surged.
Businesses are seeking individuals who can effectively analyze data, derive insights, and translate them into actionable strategies. Roles such as data analysts, business intelligence analysts, data scientists, and data engineers have become crucial in organizations of all sizes.
These professionals play a vital role in helping businesses uncover hidden patterns, identify trends, and make informed decisions. They are responsible for collecting, organizing, and analyzing data using various statistical and analytical techniques. By leveraging data visualization tools, they present complex information in a visually appealing and easily understandable format.
The rise of business analytics has also brought about the need for professionals who can work with big data. As organizations accumulate vast amounts of data from multiple sources, there is a growing demand for experts who can handle, process, and derive insights from massive datasets.
Industries such as finance, healthcare, marketing, retail, and manufacturing are actively hiring business analytics professionals to drive growth, improve operational efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. The ability to make data-driven decisions has become a critical success factor for businesses, further fueling the demand for skilled professionals in this field.
Moreover, advancements in technology, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, have accelerated the adoption of business analytics. Organizations are leveraging these technologies to automate data analysis, develop predictive models, and enhance decision-making processes.
Overall, the rise of business analytics in job opportunities reflects the increasing importance of data-driven decision-making in today's business landscape. The demand for professionals skilled in business analytics continues to grow, offering exciting career prospects for individuals with a passion for data analysis, problem-solving, and strategic decision-making.
How hr Analytics is Transforming Talent Management Strategies
HR analytics is transforming talent management strategies by leveraging data and analytics to make informed decisions about the acquisition, development, and retention of talent within organizations. Traditionally, talent management relied on subjective assessments and intuition. However, with the advent of HR analytics, organizations can now collect and analyze vast amounts of HR-related data to gain insights and make data-driven decisions.
By applying analytics to talent management, organizations can better understand employee performance, identify skill gaps, and predict future workforce needs. HR analytics enables the measurement of key performance indicators (KPIs) such as employee engagement, turnover rates, and productivity, allowing HR professionals to identify trends and patterns that impact talent management strategies.
Moreover, HR analytics provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of recruitment strategies, employee training and development programs, and performance management systems. It helps optimize workforce planning by aligning talent acquisition and development with organizational goals and objectives.
Through the use of predictive analytics, organizations can forecast future talent needs and identify potential high-performing individuals. This enables proactive talent management strategies, such as targeted development programs and succession planning, to ensure a pipeline of skilled and qualified employees.
Furthermore, HR analytics plays a crucial role in improving employee engagement and satisfaction. By analyzing employee feedback, sentiment analysis, and other data sources, organizations can identify factors influencing employee morale and take proactive measures to enhance the employee experience.
Overall, HR analytics is transforming talent management strategies by providing data-driven insights and enabling evidence-based decision-making. It helps organizations optimize their talent acquisition, development, and retention efforts, ultimately leading to a more engaged and productive workforce.
Business Analytics is an integral part of modern business operations. It aids in better decision making, improving efficiency, predicting trends, and providing competitive advantages. By mastering the relevant tools, enhancing your skills, and embracing the opportunities it provides, you can leverage the power of Business Analytics to drive business growth and personal career advancement.
From this comprehensive guide, it's clear that the value and impact of Business Analytics extend across industries and professions. Whether you're a business owner, a professional seeking career growth, or a student considering future prospects, a strong grasp of Business Analytics can open new doors of possibilities and success.
Remember, as American statistician W. Edwards Deming said, "In God we trust; all others must bring data."











































