What is Business Analytics: Power of Data
Business analytics is the practice of using data analysis and statistical methods to gain insights and make informed decisions in business settings.

Businesses face an overwhelming volume of information pouring in from various sources. Harnessing this data and transforming it into actionable insights is crucial for making informed decisions and gaining a competitive advantage. This is where the concept of Business Analytics comes into play. In this blog, we will explore the meaning, significance, and key components of Business Analytics and understand how it revolutionizes the way organizations operate.
Understanding Business Analytics
Business Analytics is a dynamic field that empowers organizations to make informed decisions by harnessing the wealth of data available to them. At its core, Business Analytics involves the systematic examination of historical data to gain insights into past performance and trends (descriptive analytics). It goes further by exploring the underlying causes of specific events (diagnostic analytics) and predicting future outcomes based on past patterns (predictive analytics). Additionally, it provides actionable recommendations to optimize decision-making (prescriptive analytics). This holistic approach enables companies to unlock the power of data-driven insights and drive strategic initiatives across various business functions.
By utilizing Business Analytics, companies can enhance operational efficiency by identifying process bottlenecks and streamlining workflows. It also enables organizations to gain valuable customer insights by segmenting audiences and understanding their preferences, leading to targeted marketing strategies and improved customer experiences. Furthermore, Business Analytics plays a crucial role in risk management by identifying potential threats and helping companies proactively mitigate them.
One of the key challenges in Business Analytics lies in data quality and integration. Accurate and comprehensive data is essential for meaningful analysis, but organizations often struggle with data from disparate sources that require integration. Addressing data privacy and security concerns is also critical when handling sensitive information.
Building a skilled workforce proficient in data science, statistical analysis, and domain knowledge is another challenge organizations face. However, overcoming this skill gap is essential to fully leverage the potential of Business Analytics.
In the face of various analytics tools available in the market, selecting the right ones that align with organizational goals and budget is crucial. Making the right choices ensures that the company can implement efficient analytics processes that deliver valuable insights.
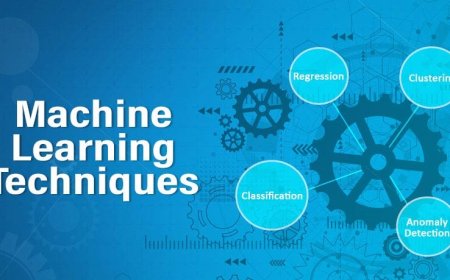
Key Components of Business Analytics
-
Descriptive Analytics: Descriptive Analytics deals with understanding and summarizing historical data to provide insights into what happened in the past. It involves basic data aggregation, data visualization, and simple statistical techniques to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. Descriptive analytics helps businesses gain a better understanding of their performance and operations, enabling them to make informed decisions based on past data.
-
Diagnostic Analytics: Diagnostic Analytics goes beyond descriptive analytics by focusing on why certain events or patterns occurred in the past. It involves performing root cause analysis and examining the relationships between different variables to understand the factors that influenced specific outcomes. By uncovering the reasons behind past performance, organizations can identify areas for improvement and optimize their processes.
-
Predictive Analytics: Predictive Analytics uses historical data and statistical algorithms to make predictions about future outcomes. It analyzes patterns and trends in past data to forecast what might happen in the future. Predictive analytics is widely used for demand forecasting, customer behavior prediction, risk assessment, and other forward-looking analyses. By anticipating future trends and events, businesses can make proactive decisions to gain a competitive advantage.
-
Prescriptive Analytics: Prescriptive Analytics takes predictive analytics a step further by providing actionable recommendations and suggesting the best course of action based on the predicted outcomes. It uses advanced algorithms and optimization techniques to identify the most optimal decisions in complex scenarios. Prescriptive analytics helps organizations make data-driven decisions by evaluating multiple options and their potential impacts.
The Role of Business Analytics in Decision-making
Business Analytics plays a pivotal role in informing and supporting decision-making processes within an organization. It involves the use of data, statistical analysis, and various analytical techniques to extract valuable insights from past and present data, which in turn guides and influences future strategic choices. Here are some key aspects of how Business Analytics contributes to decision-making:
Data-Driven Insights: Business Analytics allows decision-makers to base their choices on concrete data rather than intuition or gut feeling. By analyzing historical and real-time data, organizations gain a deeper understanding of market trends, customer behavior, and operational performance, leading to more informed and objective decision-making.
Predictive Capabilities: One of the significant strengths of Business Analytics is its ability to predict future outcomes based on historical data and statistical modeling. Predictive analytics can anticipate customer preferences, demand patterns, and potential risks, enabling proactive decision-making to seize opportunities and mitigate potential problems.
Identifying Opportunities and Threats: Business Analytics helps organizations identify new opportunities for growth and expansion. By analyzing market trends and consumer behavior, decision-makers can spot untapped markets, emerging technologies, and customer needs, leading to the development of new products or services that address these opportunities. Additionally, it can identify potential threats and challenges, allowing businesses to develop strategies to counteract or minimize their impact.
Optimizing Resource Allocation: With limited resources, organizations need to make efficient decisions on how to allocate their budgets, workforce, and other assets. Business Analytics assists in optimizing resource allocation by identifying areas where investments can yield the highest returns and allocating resources based on data-driven insights.
Performance Evaluation: Business Analytics provides valuable metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) that enable decision-makers to assess the effectiveness of their strategies and initiatives. By tracking performance against predefined goals, organizations can identify areas that need improvement and make data-driven adjustments to enhance overall performance.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: In a constantly changing business environment, decision-makers need to be aware of potential risks and uncertainties. Business Analytics aids in risk assessment by analyzing historical data and identifying patterns that can lead to potential risks. This allows organizations to develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans, minimizing the impact of adverse events.
Challenges in Business Analytics
Data Quality and Integration
One of the primary challenges in Business Analytics is ensuring the quality and integration of data from various sources. Data may be scattered across different systems and departments, leading to inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and duplications. Poor data quality can significantly impact the reliability of analysis and insights, potentially leading to flawed decision-making. Organizations must invest in data cleansing, validation, and integration processes to ensure that the data used for analysis is accurate, complete, and consistent.
Privacy and Security Concerns
As organizations gather and analyze large volumes of data, concerns about data privacy and security become paramount. Business Analytics often involves handling sensitive information, including customer data, financial records, and proprietary knowledge. The risk of data breaches and unauthorized access poses significant threats to both the organization and its customers. To address these challenges, businesses must implement robust data security measures, comply with relevant data protection regulations, and establish a culture of data privacy.
Skill Gap
The field of Business Analytics requires a skilled workforce proficient in data science, statistical analysis, data visualization, and domain knowledge. Finding individuals with a comprehensive understanding of these areas can be challenging, as the demand for such professionals often outpaces the supply. Moreover, the rapid advancements in analytics technologies necessitate continuous learning and upskilling. Organizations must invest in training and development programs to bridge the skill gap and empower their employees to harness the potential of Business Analytics effectively.
Choosing the Right Tools
With a wide array of Business Analytics tools and platforms available in the market, selecting the most suitable ones for a specific business can be overwhelming. Each tool may have its strengths and limitations, and businesses need to align their choice with their analytical requirements, budget constraints, and IT infrastructure. Additionally, integrating these tools seamlessly with existing systems and processes is another challenge that organizations must tackle to ensure a smooth analytics workflow.
Change Management and Adoption
Implementing Business Analytics within an organization often involves a cultural shift and changes in traditional decision-making processes. Some employees might be resistant to adopting data-driven insights, relying instead on intuition and experience. Effective change management strategies are essential to create a data-centric culture where analytics-driven decision-making is embraced at all levels of the organization. Education, training, and continuous support are crucial to encouraging the adoption of Business Analytics as a standard practice.
Business Analytics is the driving force behind data-driven decision-making, providing organizations with valuable insights to optimize their operations, enhance customer experiences, and stay ahead in a dynamic business landscape. By leveraging the power of data and analytics, companies can unlock new opportunities, minimize risks, and achieve sustainable growth in an ever-evolving marketplace. Embracing Business Analytics is no longer an option but a necessity for businesses seeking to thrive in the digital age.